How To Category: Comparisons, Substitutions & More
Olive Oil: A Healthier Choice
With loads of information circling the internet, and new oil products on the market, it can be difficult to choose which oil is best. The differences in oil can be attributed to 3 main factors: Fat Content, Smoke Point and Refining Process.
Fat Content:
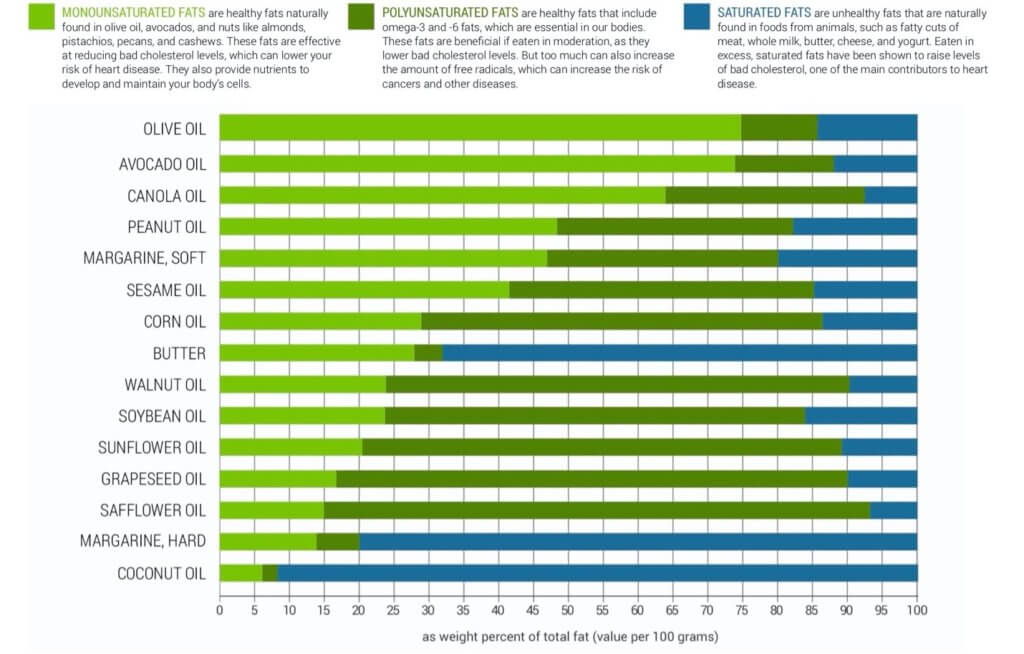
Oils are made up of two fats. See how different oils compare below.
Unsaturated fats: these are naturally found in ingredients such as olives, nuts, and avocados, and have been proven effective in reducing cholesterol levels when eaten in moderation.
Saturated fats: Naturally found in fatty foods such as meats, butter, and other dairy products. These fats have been proven to raise cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
Refining Process:
Many oils such as canola oil, or soybean oil are mixed with other oils and refined at high heats. This process removes the nutritional benefits of the oil making it a less healthy option. Filippo Berio Extra Virgin Olive Oil is un-refined, making it able to retain most of the nutrients.
Smoke Point:
A smoke point is a maximum temperature that causes oils to become unstable. Cooking with oils above their smoke point can have damaging effects on our health. Every oil has a different smoke point.
Olive Oil & Extra-Virgin Olive Oil – 356 – 437 F: These oils are best for roasting or sautéing at lower temperatures
Canola Oil – 460 F,
Unrefined Coconut oil – 350 F
Refined Coconut Oil – 450 F
Oils with higher smoke points tend to be more refined (such as canola oil) or have higher saturated fat content (such as coconut oil). Which is why many health care professionals recommend Extra-Virgin Olive Oil as an oil of choice.
Sources:
https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/olive-oil-vs-canola-oil
https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/battle-roy-oil-how-olive-oil-stacks-up-against-coconut-oil
https://www.bonappetit.com/test-kitchen/ingredients/article/types-of-cooking-oil
https://www.thespruceeats.com/smoking-points-of-fats-and-oils-1328753
Olive Oil vs. Vegetable Oil
Olive oil and vegetable oils are some of the most popular plant oils used around the globe, each having unique characteristics. But the question we ask ourselves is which one should we use and why?
Olive oil has been known for its health benefits including improved heart health and immune system performance, in addition to a decreased risk of chronic disease. But why do some people still prefer to use vegetable oil for frying and baking?
Before we start comparing the two oils, let’s take a look at how they are made. Olive oil is made from pressed olives. Extra-virgin olive oils in particular are the least processed, meaning they retain the most beneficial nutrient compounds. On the other hand, vegetable oil is made by mixing oils from different sources, such as canola, cottonseed, sunflower, soybean, corn, and safflower.
Unlike olive oil, vegetable oil requires more processing to remove impurities and create a neutral-flavored blend. Although the processing of the vegetable oil creates a neutral flavor that many prefer, it also removes healthful antioxidants.
Now to answer your question, let’s clear the misconception that exists around using olive oil for frying and baking. Vegetable oils have a smoke point of 460°F. Extra virgin olive oils have a smoke point of around 392°F. Further, the level of harmful polyunsaturated fats in vegetable oils are much higher than those of olive oils (61% VS 9%). According to a study published by ACTA Scientific Nutritional Health, refined oils higher in polyunsaturated fats proved to be less stable under high temperatures and oxidized much more quickly than oils lower in polyunsaturated fats. The study compared ten of the most commonly used oils and found that extra virgin olive oil is the most stable cooking oil.
As a general rule, all olive oil is a healthy choice. The more flavor the olive oil has for example Filippo Berio Extra Virgin Olive Oil, means the oil had the least amount of processing, meaning there are more potential health benefits it has due to the unique olive antioxidants and polyphenols.
However, if you prefer to use a neutral-flavored cooking oil while maintaining the health benefits of olive oil, use Filippo Berio Olive Oil or Filippo Berio Extra-Light Olive Oil for a more neutral flavor, while still reducing the level of polyunsaturated fats and retaining some anti-oxidants. And always remember, olive oil can take the heat!
Sources:
https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/olive-oil-vs-vegetable-oil
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/olive-oil-vs-vegetable-oil#differences
Are All Olive Oils Healthy?
Have you ever wondered if there is a type of olive oil healthier than the other? It is common knowledge that extra virgin olive oil reduces the risk of heart disease. But did you know that non-virgin olive oil is also heart healthy?
According to the FDA, olive oil is heart healthy regardless of whether it was extra virgin or not.
The heart benefits of olive oil are attributed to the fatty acids. For example, extra virgin olive oil has more phenols than regular olive oil but the same high monounsaturated fatty acid content.
The phenols in extra virgin olive oil are associated with a wide range of health benefits such as cancer prevention, improvements in metabolism, and reduction of inflammation. But non-virgin olive oil has also proven to improve heart health.
Filippo Berio Extra Virgin Olive Oil VS Olive Oil VS Extra Light Olive Oil
Made from the first cold pressing of the finest olives, Filippo Berio Extra Virgin Olive Oil has a distinctly rich taste and fresh aroma with subtle notes of olive. We suggest using it for salad dressings, sauces, and gravies, drizzling over pasta, and marinating or sautéing fish & vegetables. It has a smoke point of 338°F – 374°F.
Exquisitely balanced, Filippo Berio Olive Oil can be used to enhance the true flavor of any dish. It has a mild flavor with gentle hints of olive and a smoke point of 356°F – 392°F.
We recommend using it to baste meats and fish, sautéing meats, pizza dough, and focaccia, roasting meats, fish, and vegetables.
Last but not least, Filippo Berio Extra Light Olive Oil has an exceptionally high smoke point of 410°F – 446°F, making it the ideal choice for frying, stir-frying, and baking your favorite foods. It has a subtle flavor profile with a faint hint of olive.
Source:
https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/is-non-extra-virgin-olive-oil-heart-healthy
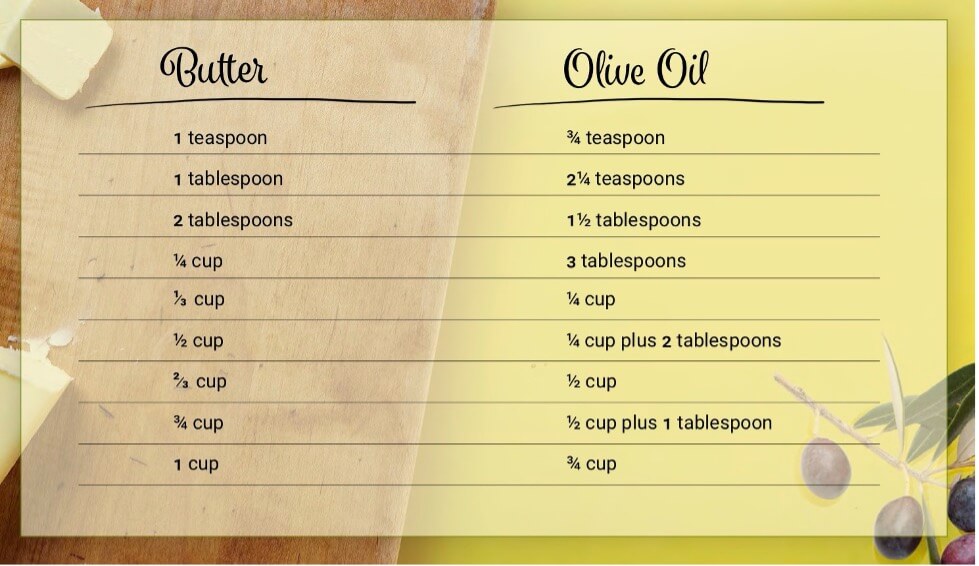
Baking with Olive Oil: How to Swap out Butter
Made with over 50% saturated fats, by now it is no surprise that we should be trying to limit our butter intake. Saturated fats are unhealthy fats found in animal products such as fatty cuts of meat, whole milk, cheese and butter. They have been shown to raise cholesterol, which is one of the main contributors to heart disease!
But not to fear, it is still possible to create all your favorite baked goods without the butter! In baking, when a recipe calls for melted butter or any neutral cooking oil simply swap it for Filippo Berio Extra-Light Olive Oil. Olive oil, unlike many other oils and butter, is made up of primarily unsaturated (healthy) fats including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fats have proven to lower cholesterol and risk of heart disease. Swapping out butter for olive oil is a simple way to make a healthy swap without sacrificing any flavor!
Filippo Berio Extra-Light Olive Oil has a subtle, flavor with an exceptionally high smoke point making it ideal for baking. In fact, the smoke point of Extra-Light Olive Oil is higher than butter, making it a healthier option to cook with.
Make your favorite recipes below – all the flavor and decadence without the saturated fat!
Traditional Recipes: Apple Caramel Pie, Double Chocolate Cake, Carrot Cake with Mascarpone Frosting
Lighter Desserts: Baked Doughnuts with hidden Veggies, Zucchini Muffins, Balsamic Berry Crumble